Wuhan Combination Center
Established: 2024
Chair: Jianghui Geng
Mailing List: Wuhan Combination Center Mailing List
Charter
The Wuhan Combination Center (WCC) was formally approved by the IGS Governing Board (GB) as a Pilot Project (PP) in 2024. It aims at providing combined high-precision and highly-reliable multi-GNSS satellite orbits/clocks/biases and receiver clocks/biases. The priorities of the WCC include the development and exploitation of innovative combination efforts for orbits, clocks, and code/phase biases as an experimental alternative to the legacy combination procedure.
The tasks of the WCC are as follows. (1) The WCC will focus on combining orbit, clock, and code/phase bias products, covering ultra-rapid, rapid, and final product lines. (2) Combined products for GPS, GLONASS, and Galileo will be released initially and BDS/QZSS will be introduced later. (3) Quality control for the legacy combination products and continuous exchange with the ACC. (4) PPP-AR validation will be carried out to monitor the quality and reliability of the available combined products. The WCC will enhance the consistency, interoperability, and reliability of AC-specific GNSS products, addressing the challenges in areas such as time and frequency transfer, geodesy, and satellite positioning.
Goals
- Towards stable multi-GNSS orbit/clock/bias product combination over all frequencies.
- Ensure a minimum availability of 95% for ultra-rapid and rapid combined products, and over 99% for final combined products.
- Cross-validate with available AC and combined products.
- Facilitate PPP-AR by integrating phase bias products into the combination process.
- Ensure day-boundary continuity of combined products to deliver more stable services for time and frequency transfer.
- Disseminate combined products to the GNSS community to support geodetic, geophysical, and timing applications.
Membership
Name |
Affiliation |
Role |
|---|---|---|
| Jianghui Geng | SKLPG, CAS | Coordinator |
| Qiang Wen | SKLPG, CAS | Lead of clock/bias combination |
| Guo Chen | Wuhan University | Lead of orbit combination |
| Yahao Zhang | SKLPG, CAS | Clock/bias combination and web developer |
The WCC Pilot Project’s initial membership is described in the table above. Additional personnel, both in active and in advisory roles, and from diverse geographic areas, are welcomed.
Download address for WCC precision satellite products:ftps://bdspride.com/wcc/wwww/
Simple script: curl –ftp-ssl -k -O “ftps://bdspride.com/wcc/${week}/${filename}”
Where week and filename represent the GPS week and filename respectively.
For example:
week=2369
filename=WCC0OPSFIN_20251580000_01D_01D_OSB.BIA.gz
Combination and analysis of rapid satellite products
The rapid satellite orbit/clock/bias products provided by different ACs are combined and evaluated.
These products are accessed from the CDDIS archive (https://cddis.nasa.gov/archive/gnss/products/) and the corresponding ACs are listed in the following table.
Label |
Rapid | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| system | orbit | clock | attitude | code OSB | phase OSB | Note | ||||
| COD0OPSRAP | GRE | 300 s | 30 s | 30 s | 1 d (GE) | 1 d (GE) | ||||
| EMR0OPSRAP | GR | 300 s | 300 s | |||||||
| ESA0OPSRAP | GR | 300 s | 30 s | |||||||
| GFZ0OPSRAP | GRE | 300 s | 300 s | |||||||
| GRG0OPSRAP | GE | 300 s | 30 s | 30 s | 1 d (GE) | 1 d (GE) | ||||
| HUS0MGXRAP | GRE | 300 s | 30 s | 30 s | 1 d (GRE) | 1 d (GE) | ||||
| IGS0OPSRAP | G | 900 s | 300 s | Comparison only | ||||||
| JGX0OPSRAP | GRE | 300 s | 30 s | Comparison only | ||||||
| JPL0OPSRAP | GE | 300 s | 30 s | 30 s | ||||||
| NGS0OPSRAP | G | 300 s | ||||||||
| SIO0OPSRAP | G | 900 s | ||||||||
| WUM0MGXRAP | GRE | 300 s | 30 s | 30 s | 1 d (GRE) | 1 d (GE) | ||||
| Note: a. GRE stands for GPS, GLONASS and Galileo, respectively. b. OSB stands for observable-specific signal bias. c. In the combination and analysis, rapid products from AC are represented using their ID + “r”, e.g., “CODr” is for the rapid products from COD. |
||||||||||
Orbit combination results
For the methodology employed in the orbit combination, please refer to “Chen et al., (2023) Multi-GNSS Orbit Combination at Wuhan University: Strategy and Preliminary Products. J Geod. 97, 41”.
The GNSS rapid orbit products are combined with a sampling rate of 300 s. All products are combined on daily basis, with a latency of three days. All results are presented on weekly basis, with a latency of one week.
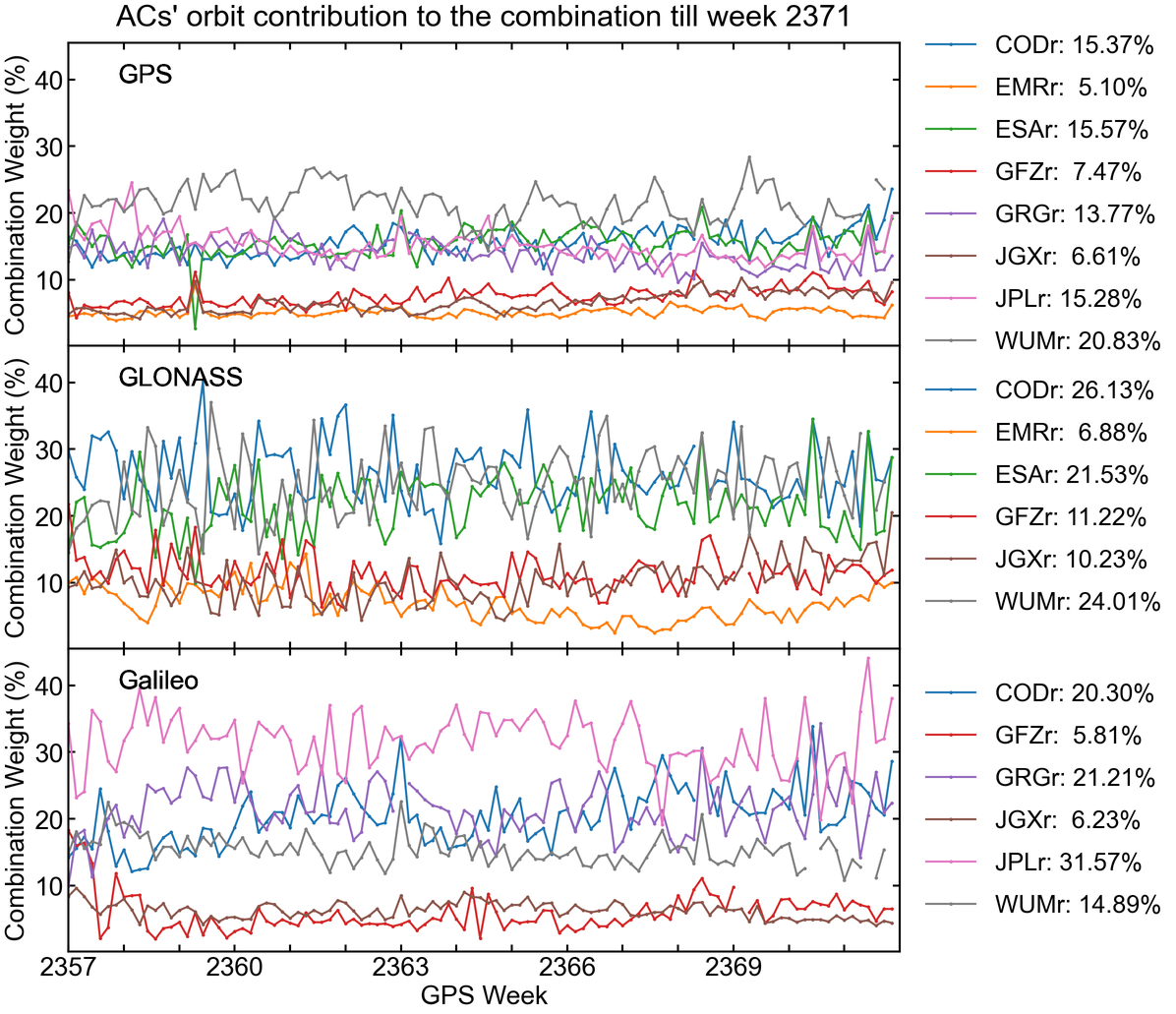
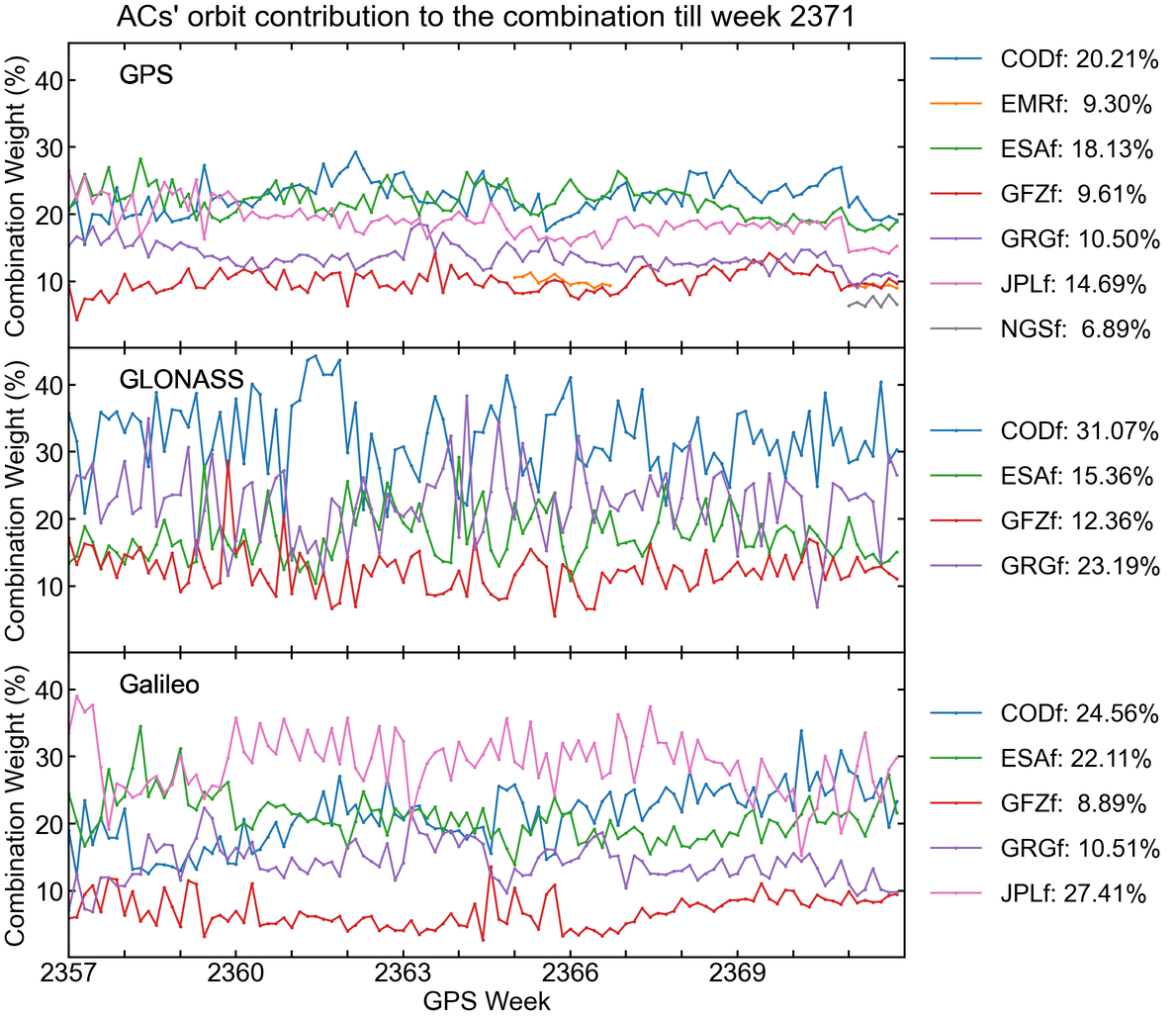
Orbit combination weight
The orbit combination employs an AC-specific and constellation-specific weighting strategy in which the weight assigned to a particular product depends on its consistency in relation to the combined orbit.
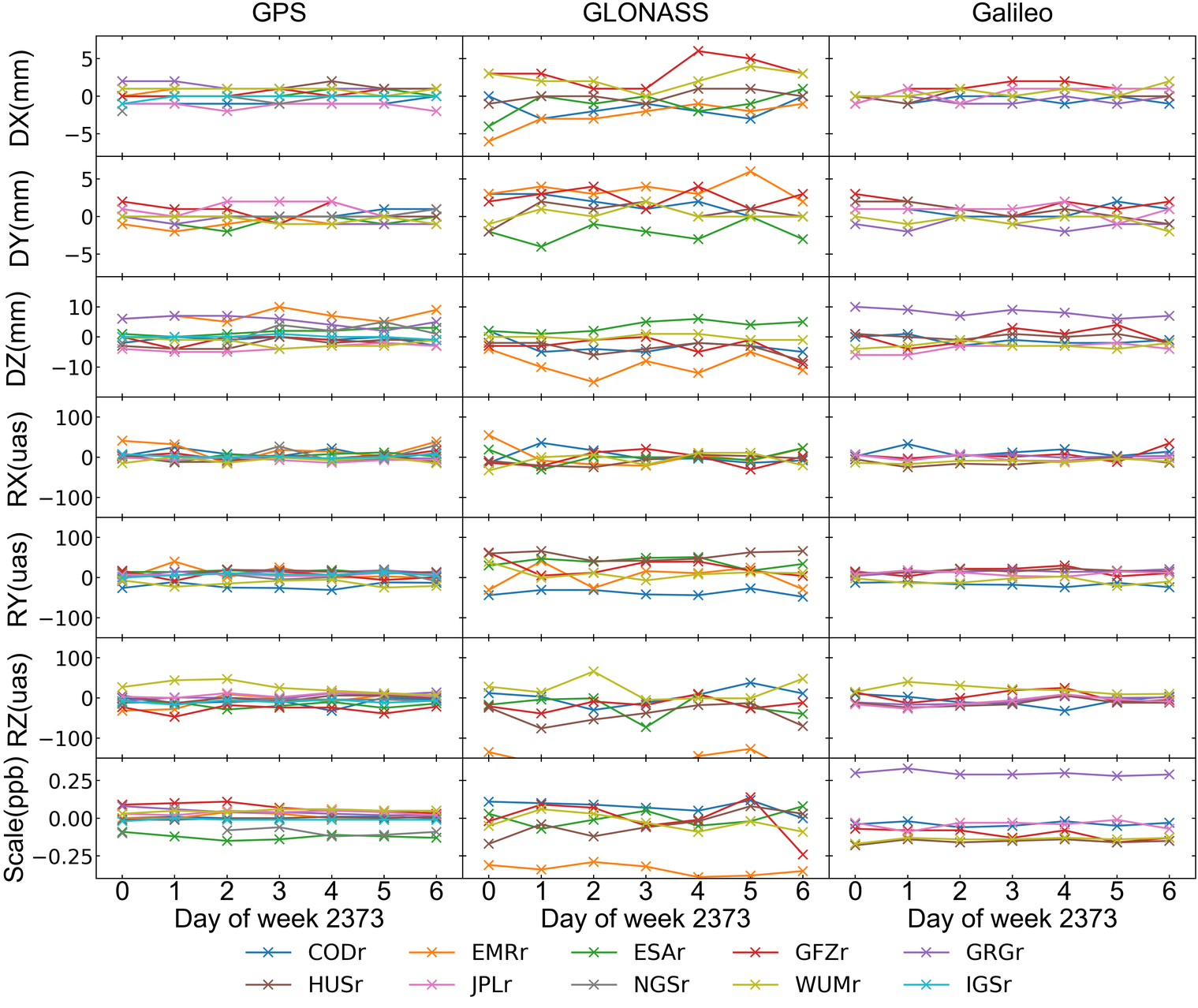
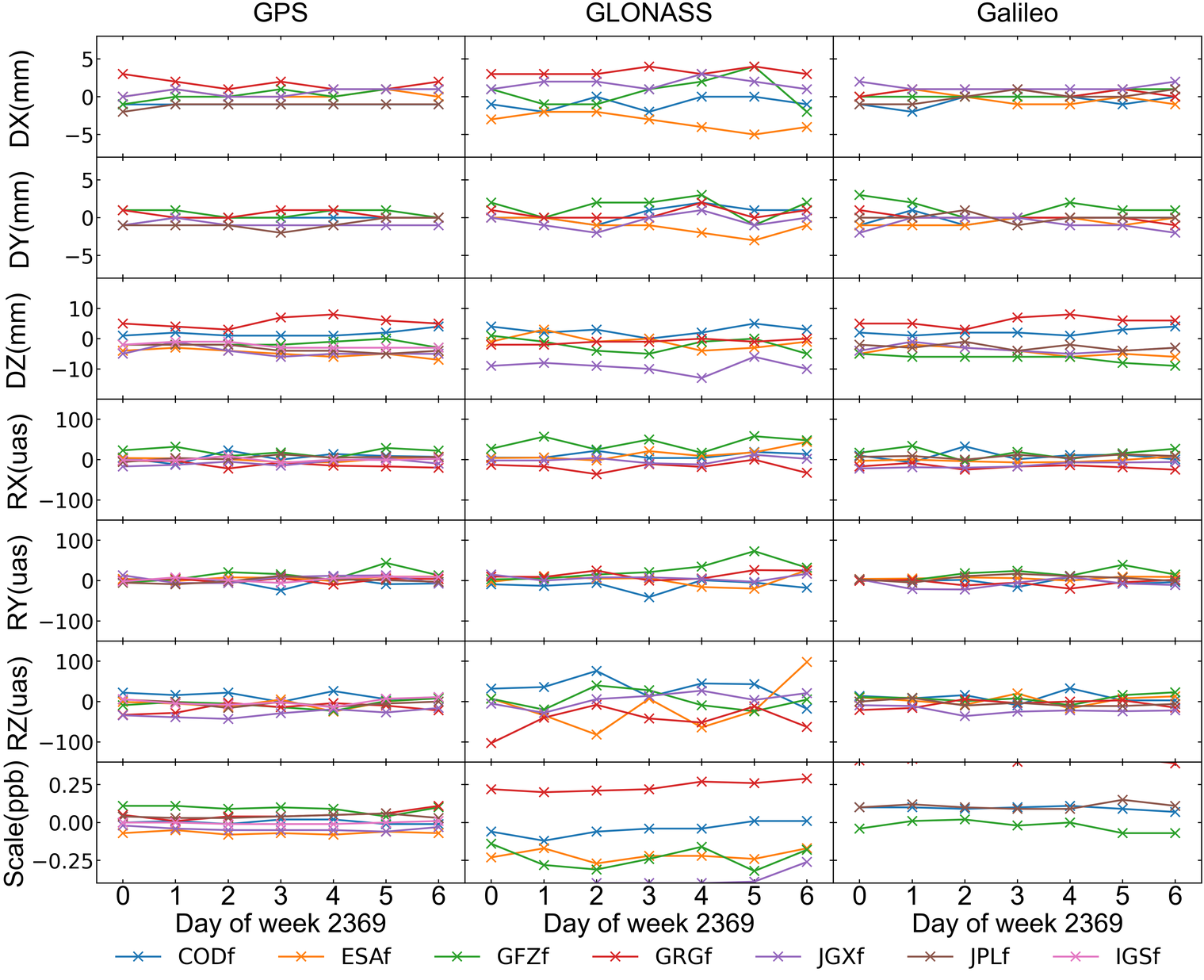
ACs’ orbit transformation parameters
The differences between AC-specific satellite orbits and the combined orbits are expressed in terms of seven Helmert parameters.
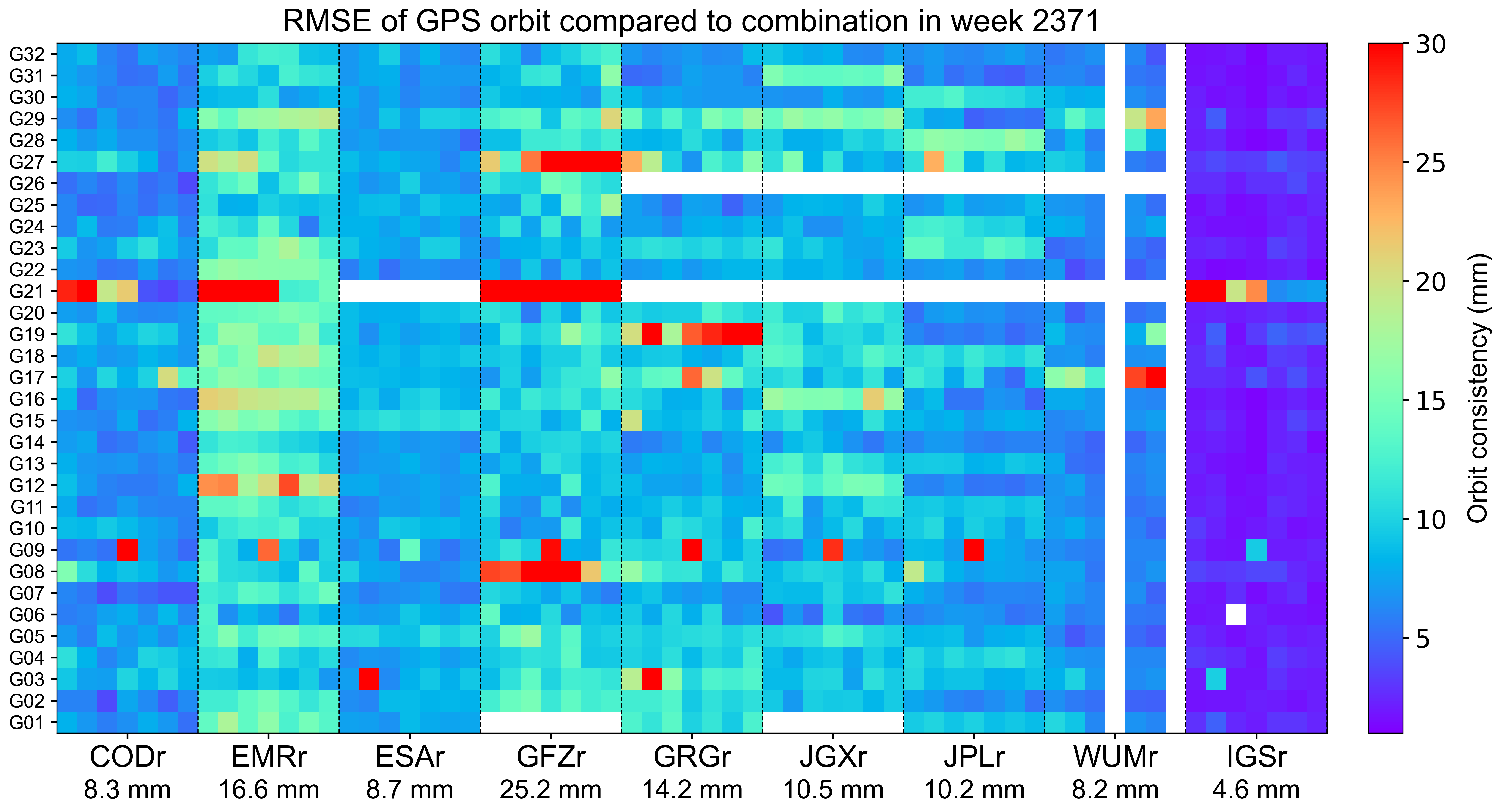
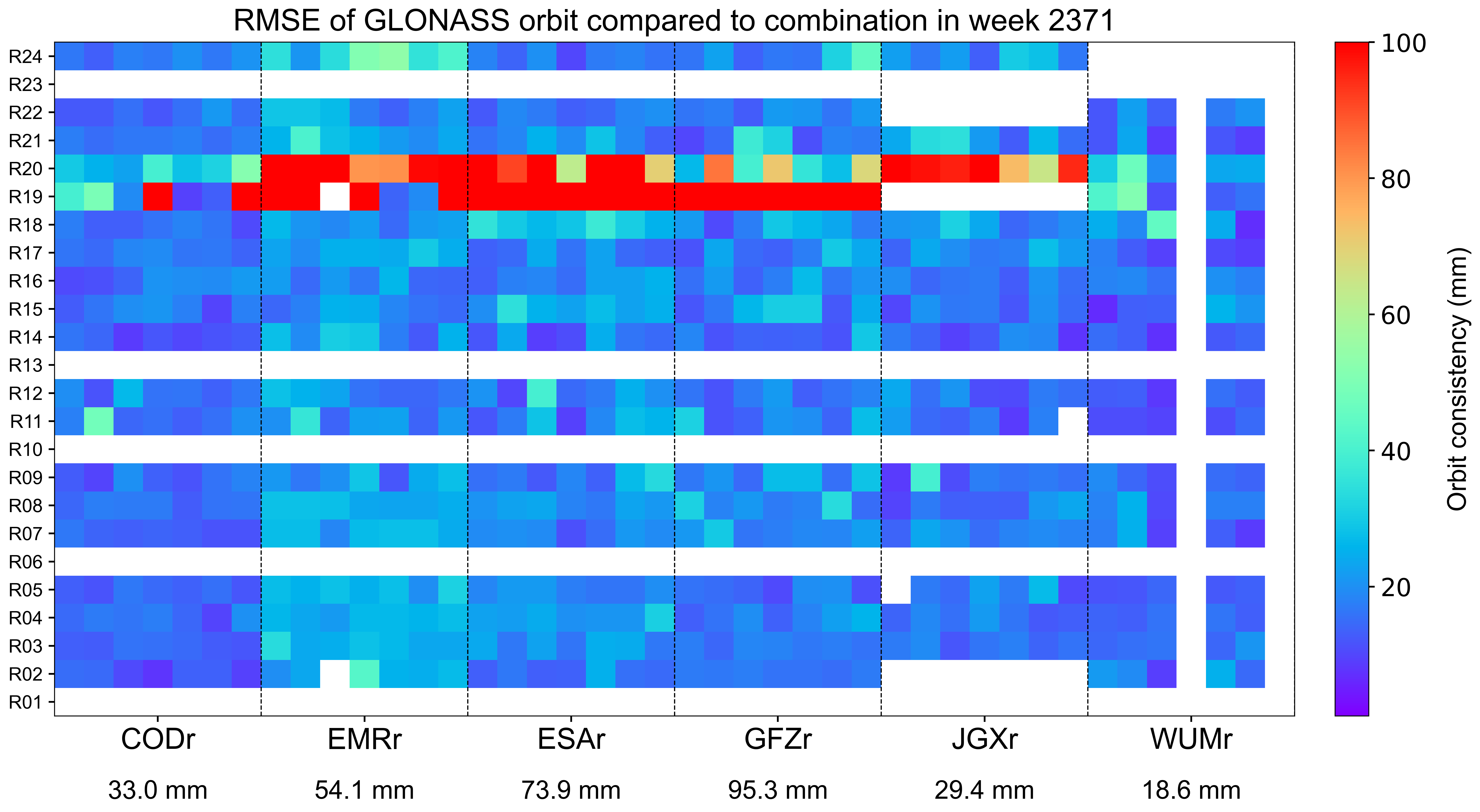
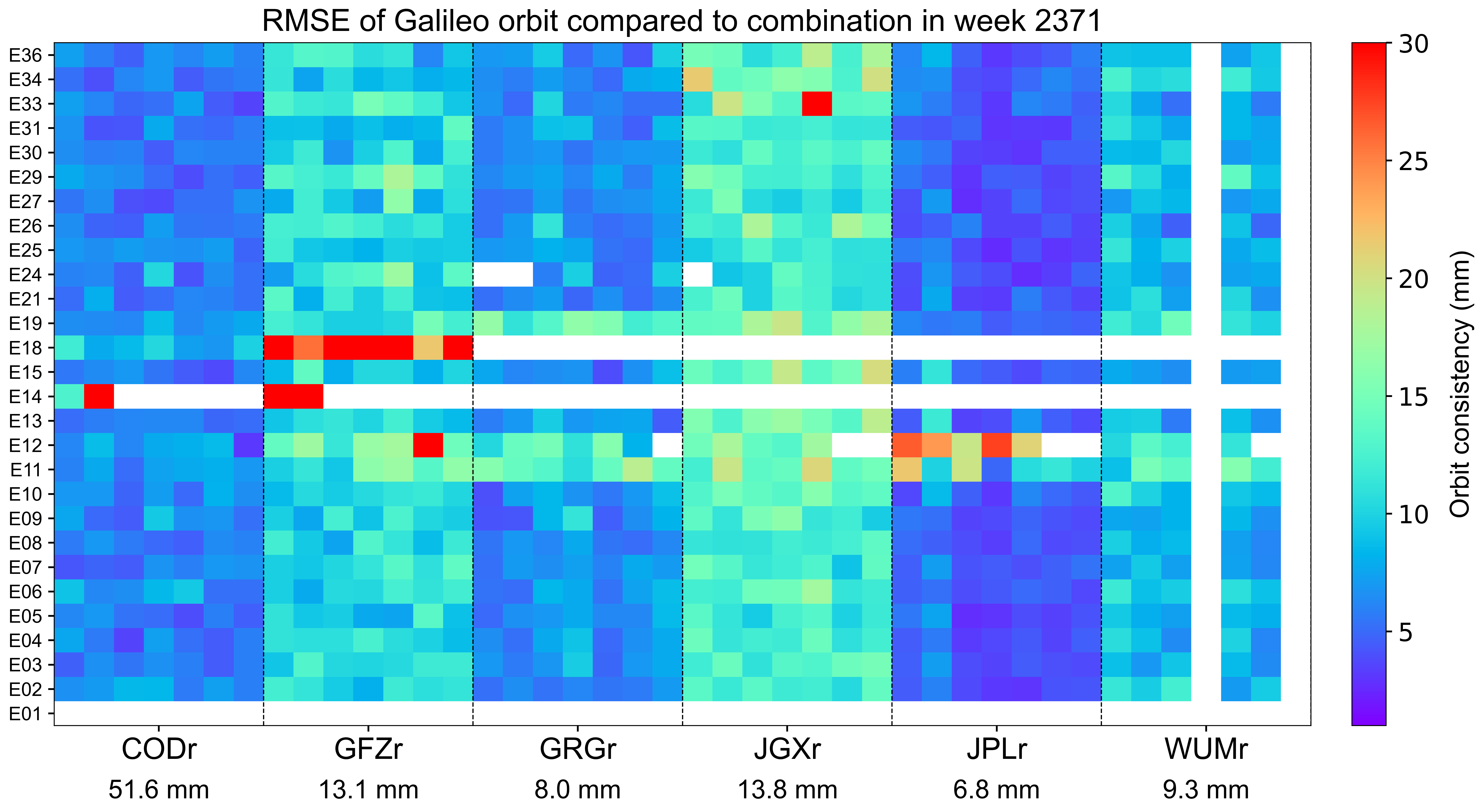
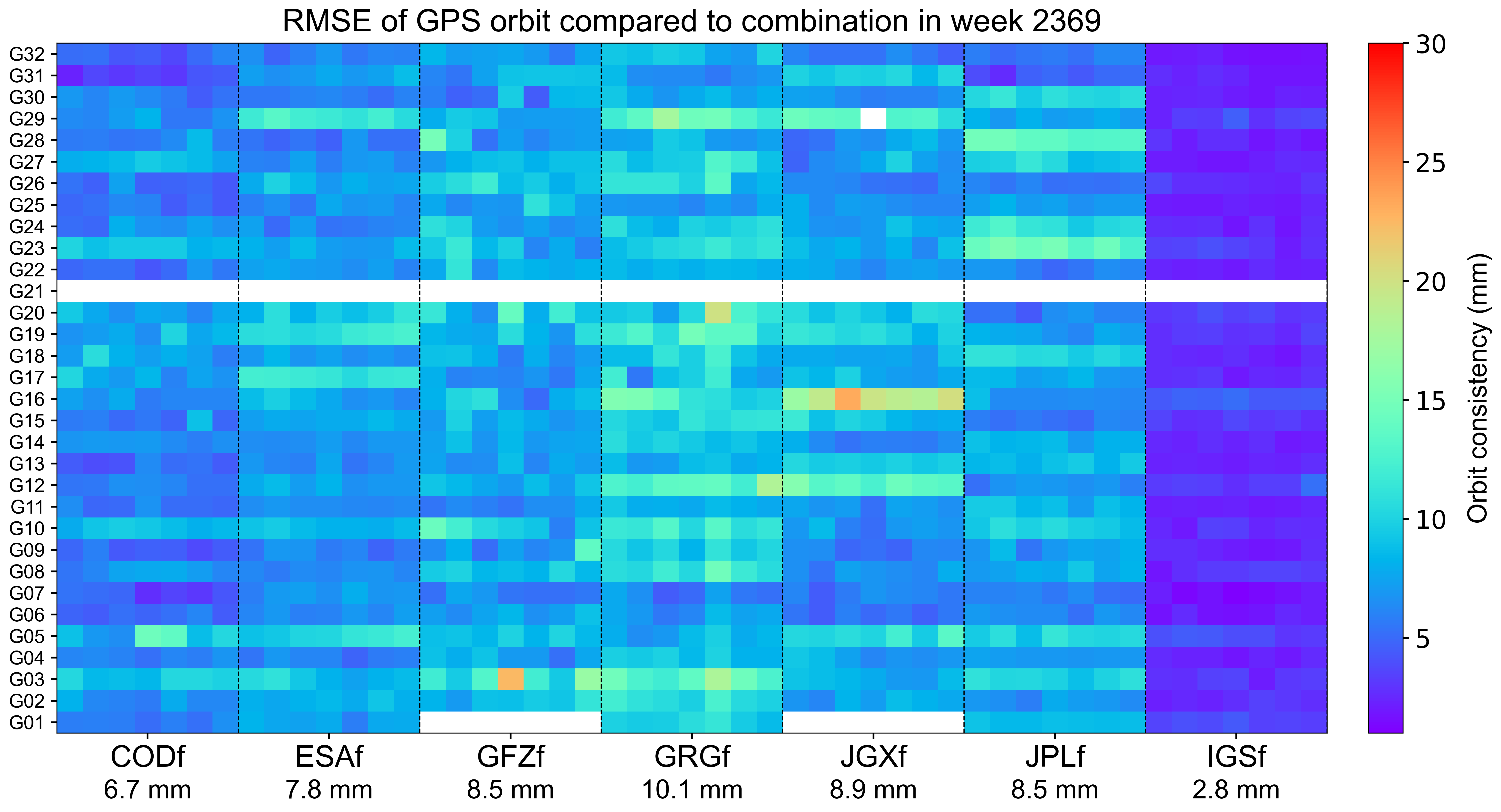
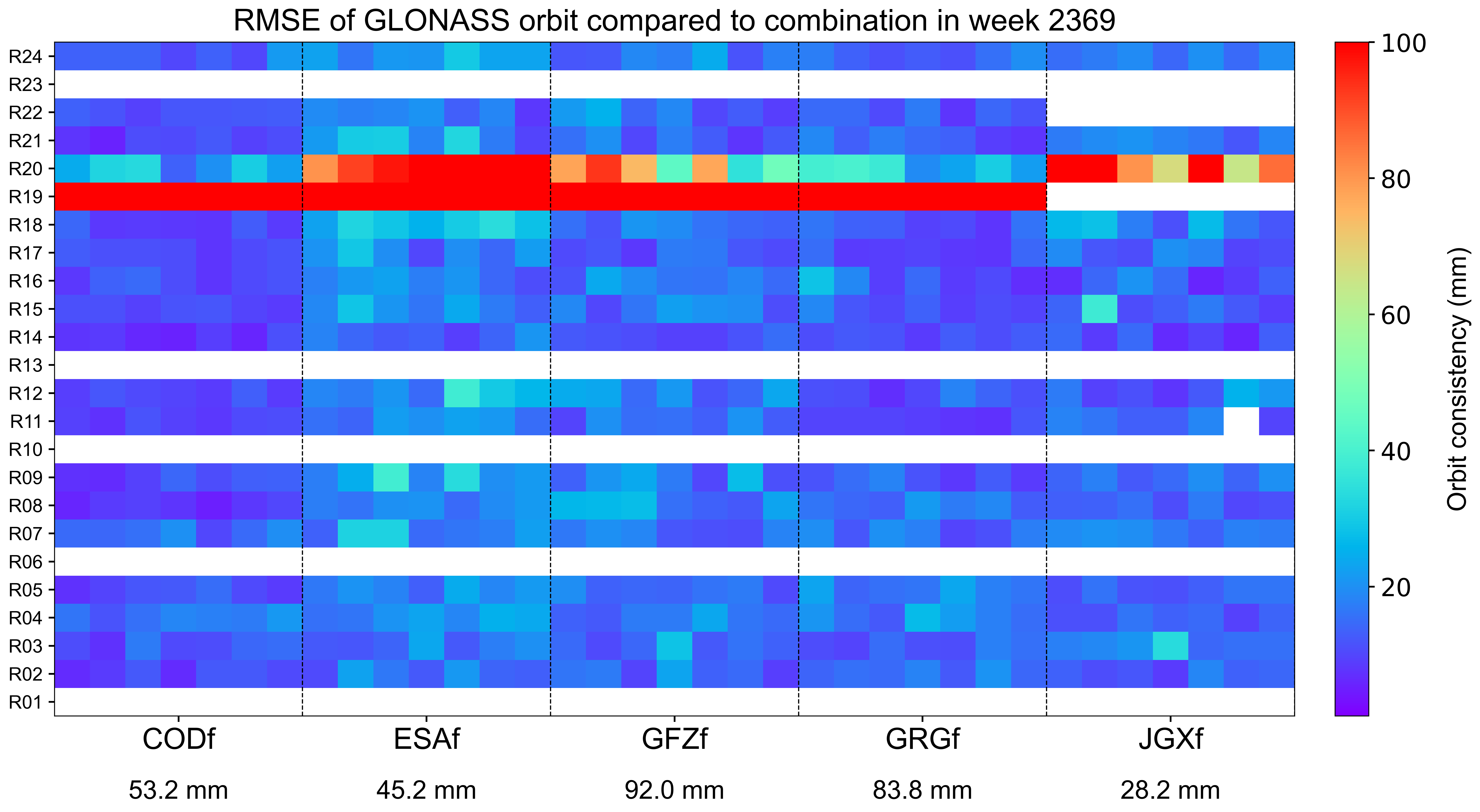
The weekly orbit RMSE
The orbit RMSE refers to the daily RMSE of orbit for each AC with respect to the combined orbit, which reflects the precision of orbit combination and the consistency between individual ACs. Each grid represents a satellite on a particular day. Blank grids mean unavailable products and a slash inside means an outlier excluded from the combination. The statistics at the bottom indicate the overall RMSE of AC orbit for this week.
Clock/bias combination results
For the method used in the clock/bias combination, please refer to “Geng et al., (2024) Integrated satellite clock and code/phase bias combination in the third IGS reprocessing campaign. GPS Solut. 28, 150”.
The combined orbit products are used as the reference, and the reference attitude is generated by the open-source software GROOPS from TUGraz. The GNSS rapid clock products are combined with a sampling rate of 30 s. All products are combined on daily basis, with a latency of three days. All results are presented on one weekly basis, with a latency of one week.
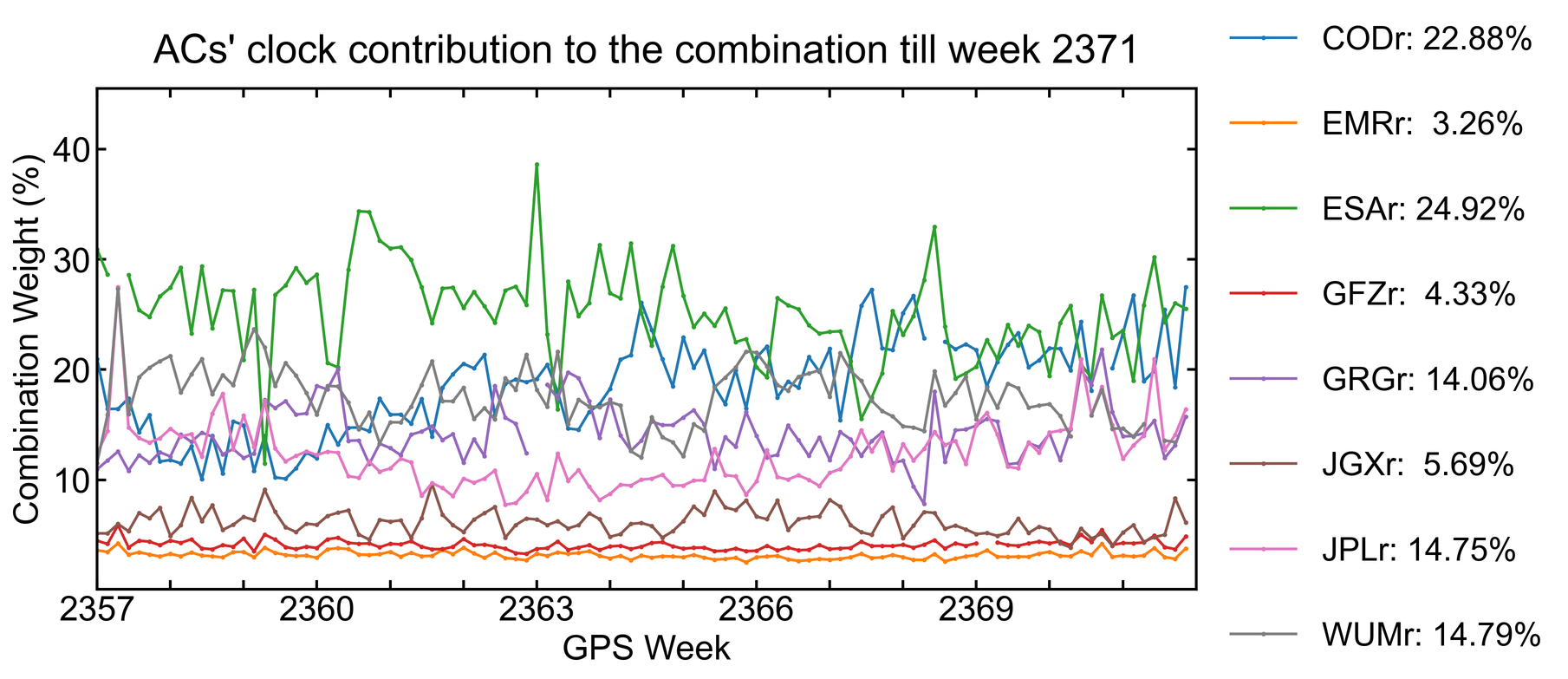
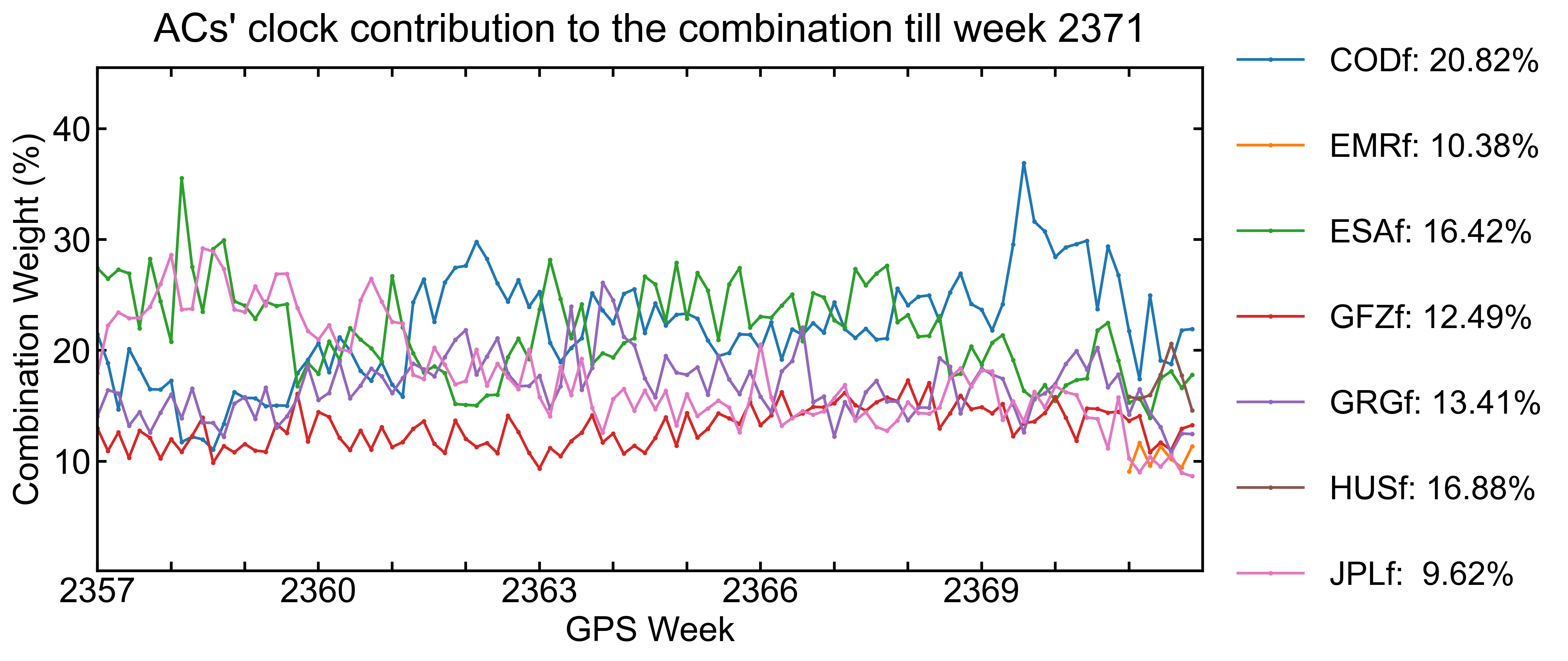
Clock/bias combination weight
The clock/bias combination employs an AC-specific weighting strategy in which the weight assigned to a specific product depends on its residuals in relation to the combined clock.
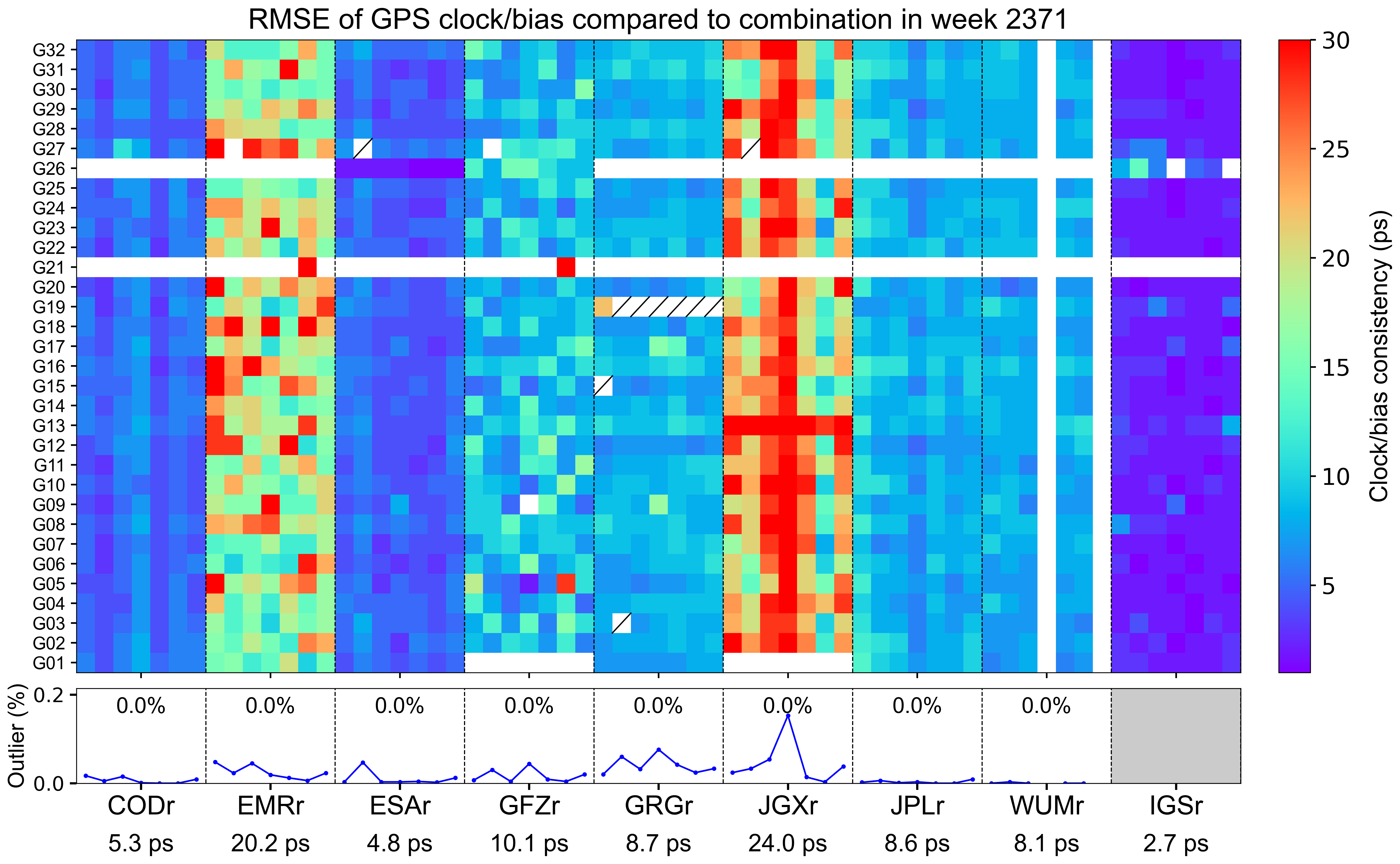
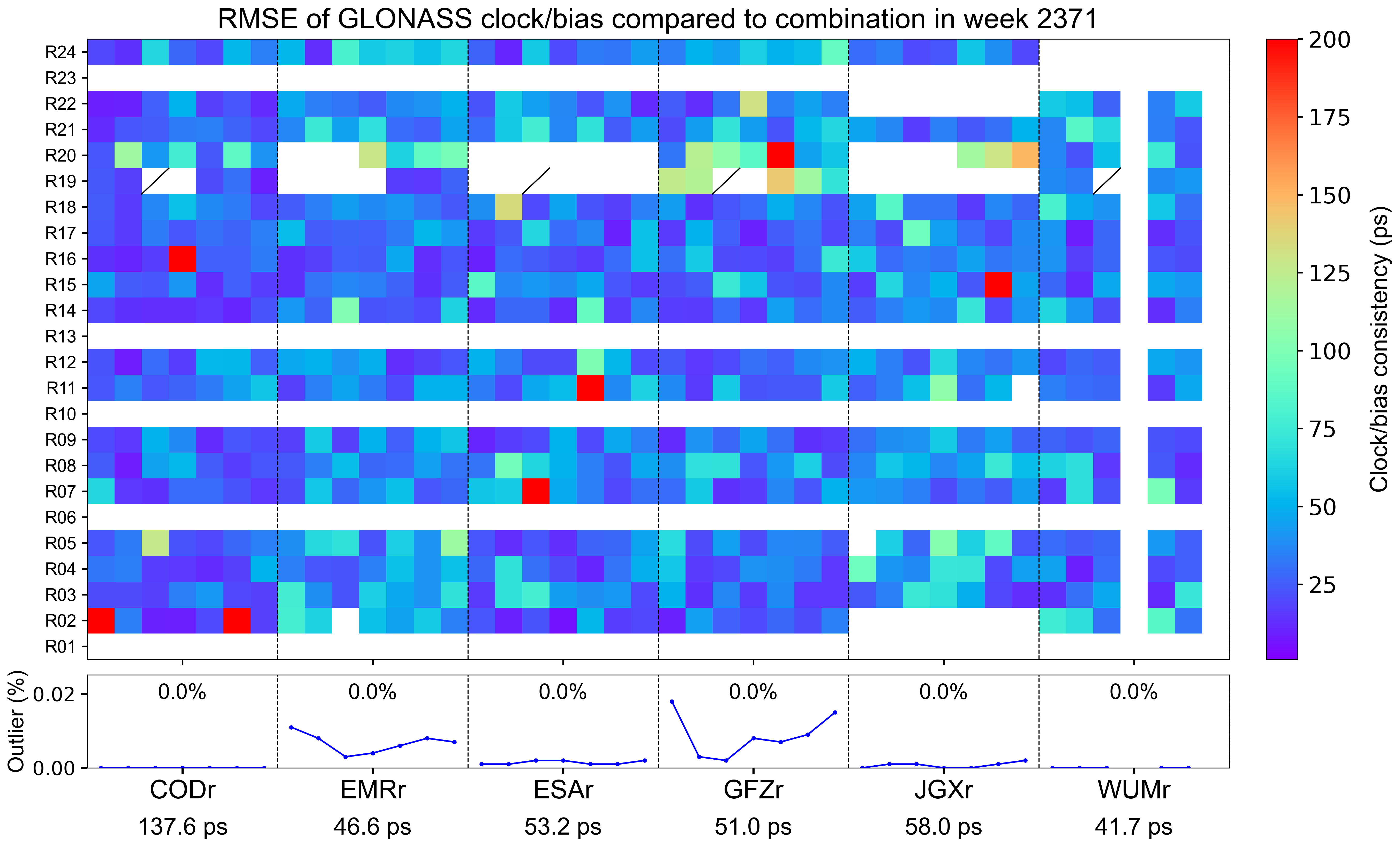
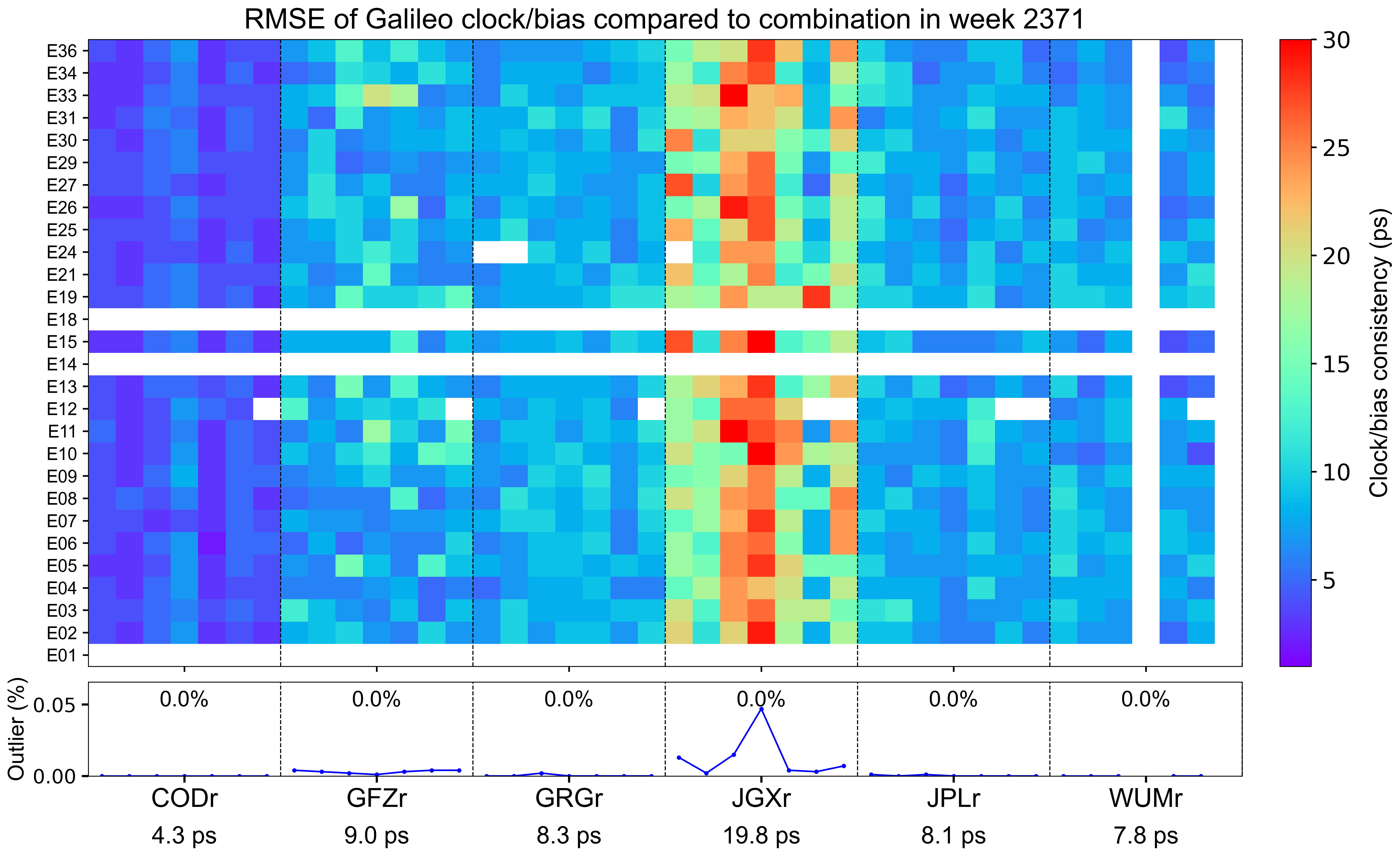
The weekly clock/bias RMSE
The clock/bias RMSE refers to the daily combination residuals’ RMSE for each AC with respect to the combined integer clock, which reflects the precision of clock/bias combination and the consistency among contributing ACs. Each grid represents a satellite on a particular day. Blank grids mean unavailable products and a slash inside means an outlier excluded from the combination. The line chart below shows the outlier rate of satellite clocks per day for each AC, with gray blocks indicating that relevant satellite clocks do not contribute to the combination. The statistics at the bottom indicate the overall RMSE of AC-specific clock/bias products for this week.
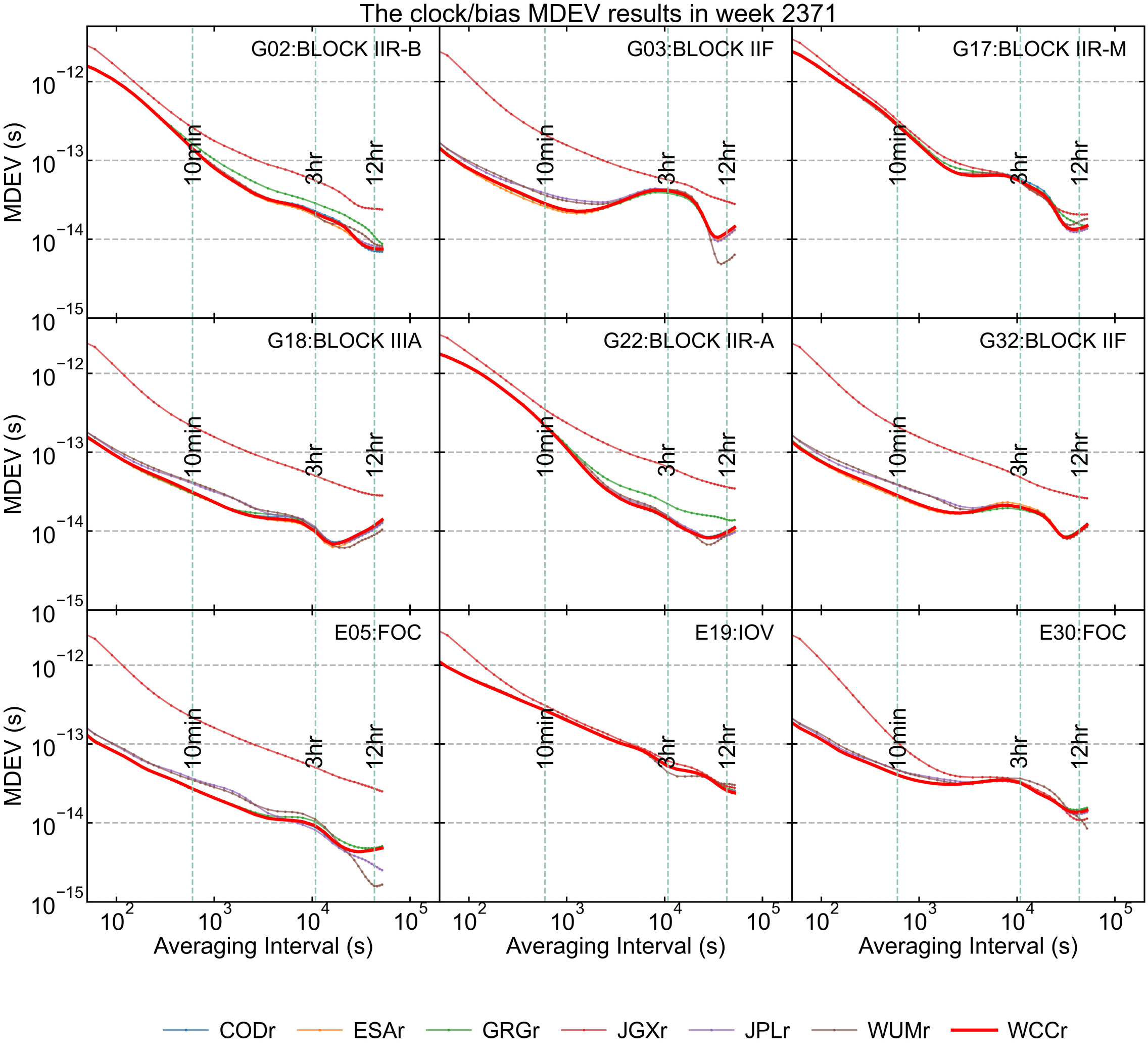
The clock/bias Allan Deviation
The Modified Allan Deviation (MDEV) is used to characterize the frequency stability and noise properties of the integer(legacy) clocks over a week. We present the MDEV values of several representative satellites and stations from each AC and the WCC products. The smaller the MDEV, the better the stability of the clock products. Note that only clock products are used when bias files are unavailable; EMR and GFZ solutions were excluded from the analysis due to their 5-minute sampling interval; the GLONASS satellites marked in red only represent legacy clock.
PPP/PPP-AR validation
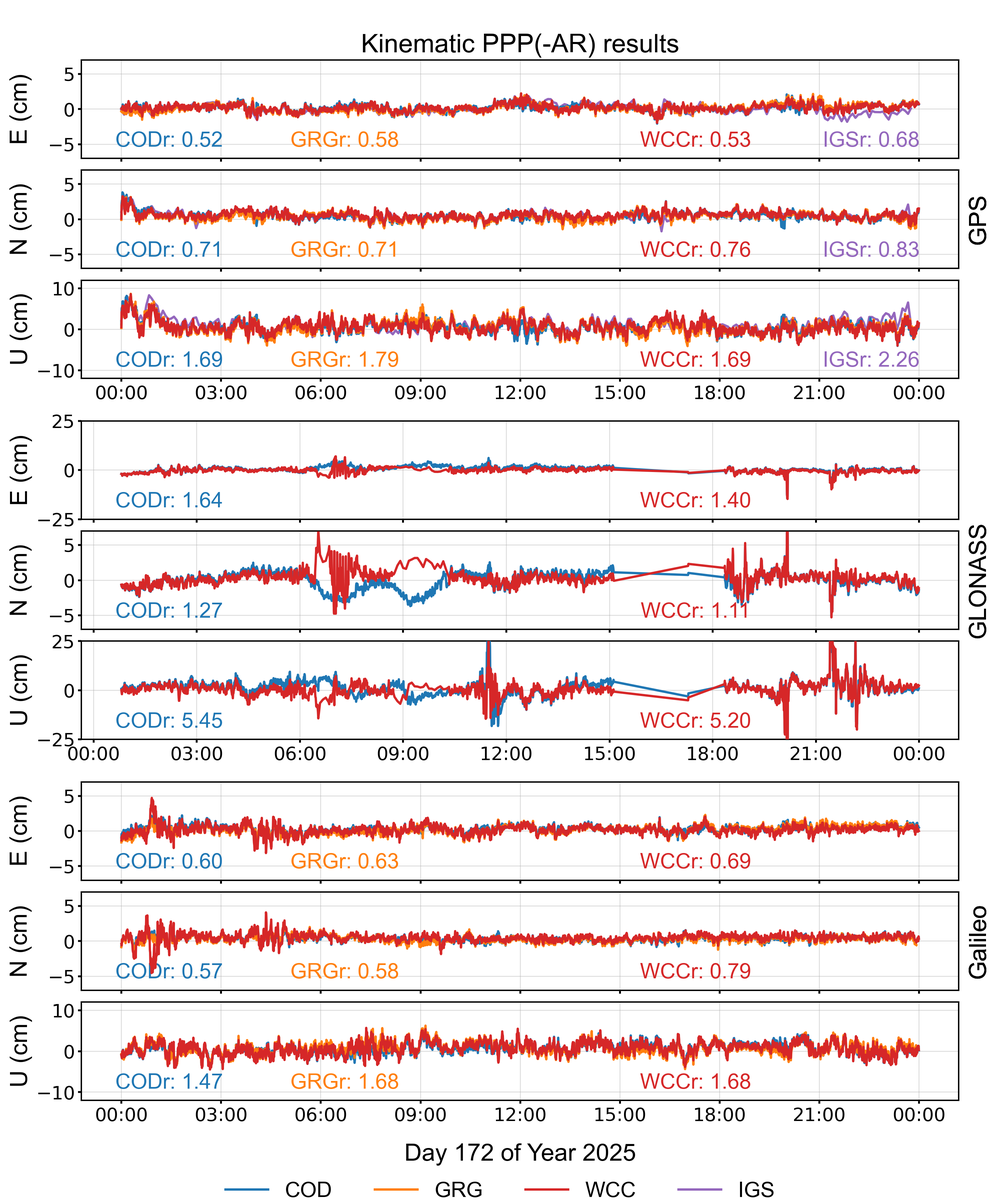
Kinematic PPP/PPP–AR validation
The GPS/GLONASS/Galileo data with a sampling rate of 30 s from one randomly selected IGS station are processed for PPP/PPP-AR in a kinematic mode with the PRIDE PPP-AR software. This picture shows the kinematic positioning accuracy on the last day of this week. IGS daily SINEX products are used as reference solution. “WCC” stands for the combined products.Note that only IGS data are processed at a sampling rate of 300 s.
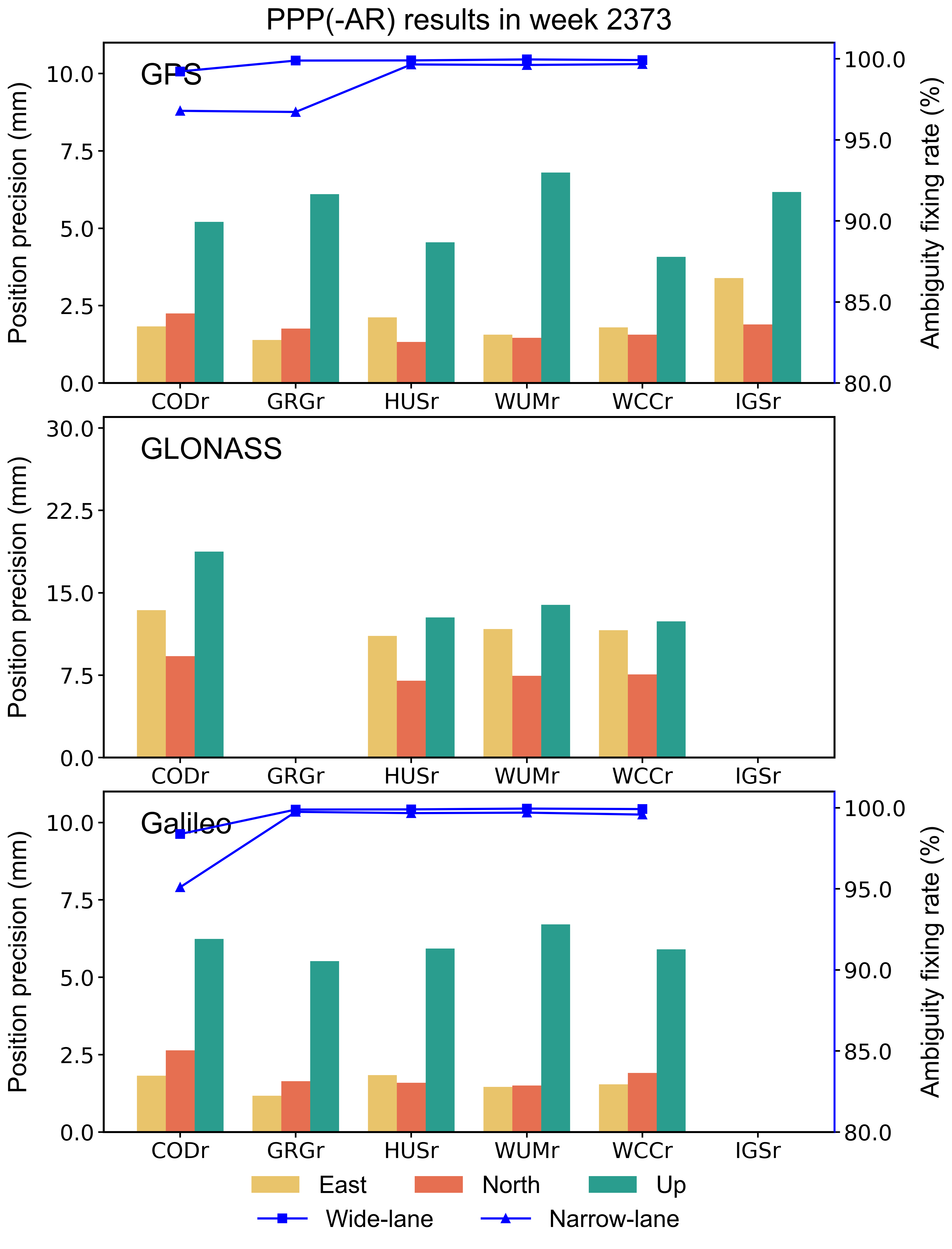
Static PPP/PPP-AR validation
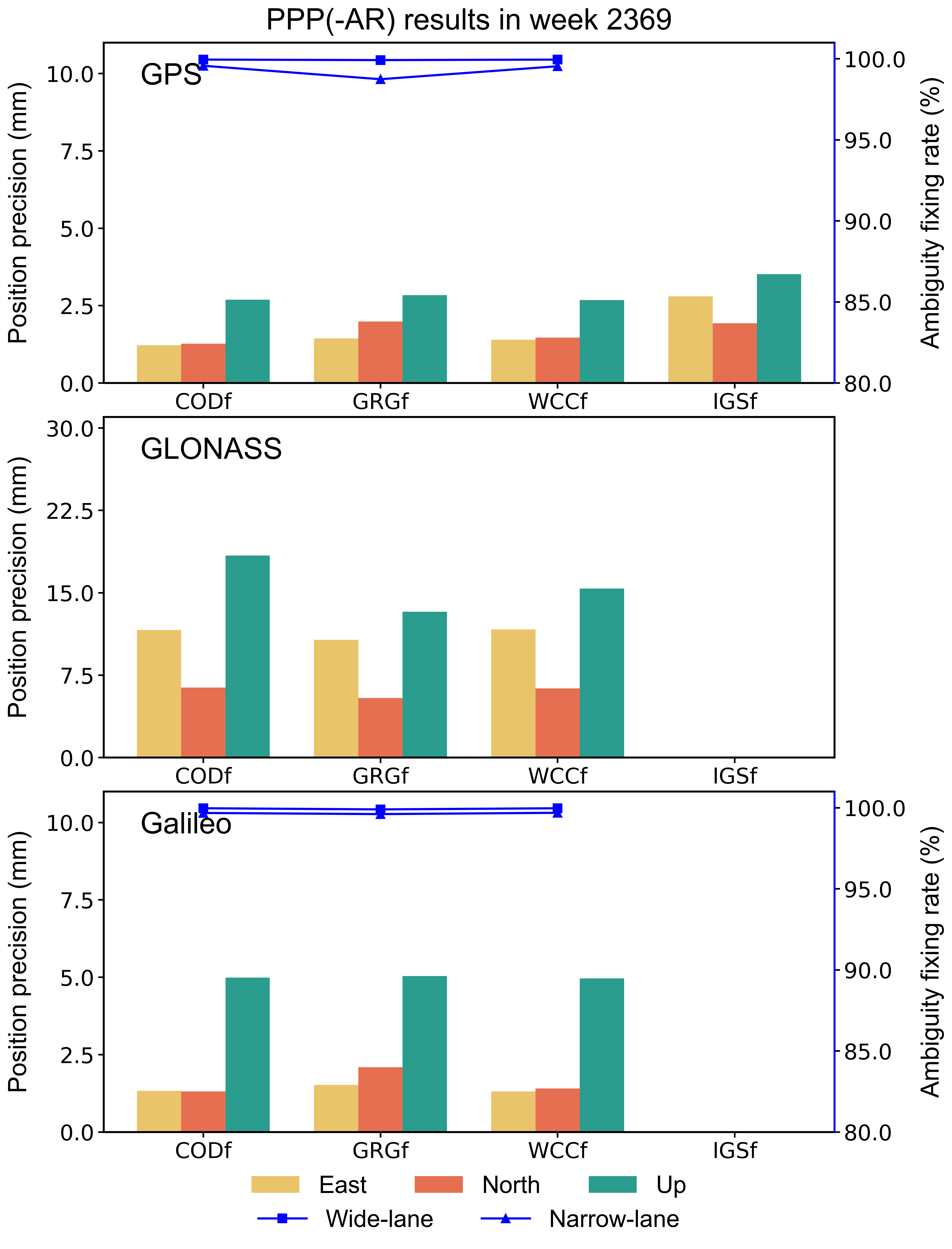
The GPS/GLONASS/Galileo data with a sampling rate of 300 s from 10 globally distributed stations are processed for PPP/PPP-AR in a static mode with the PRIDE PPP-AR software. The fixing rate and position precision of each single constellation solution are presented in the figure below. IGS daily SINEX products are used as reference solution. “WCC” stands for the combined products.
Combination and analysis of final satellite products
The final satellite orbit/clock/bias products provided by different ACs are combined and evaluated.
These products are accessed from the CDDIS archive (https://cddis.nasa.gov/archive/gnss/products/) and the corresponding ACs are listed in the following table.
Label |
Final | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| system | orbit | clock | attitude | code OSB | phase OSB | 24:00 epochs | Note | |||
| COD0OPSFIN | GRE | 300 s | 30 s | 30 s | 1 d (GE) | 1 d (GE) | CLK&SP3 | |||
| EMR0OPSFIN | G | 300 s | 30 s | 30 s | 1 d (G) | 1 d (G) | ||||
| ESA0OPSFIN | GRE | 300 s | 30 s | SP3 | ||||||
| GFZ0OPSFIN | GRE | 300 s | 30 s | |||||||
| GRG0OPSFIN | GRE | 300 s | 30 s | 30 s | 1 d (GE) | 1 d (GE) | CLK&SP3 | |||
| HUS0MGXFIN | GRE | 300 s | 30 s | 30 s | 1 d (GRE) | 1 d (GE) | CLK&SP3 | |||
| IGS0OPSFIN | G | 900 s | 30 s | Comparison only | ||||||
| JGX0OPSFIN | GRE | 300 s | 30 s | SP3 | Comparison only | |||||
| JPL0OPSFIN | GE | 300 s | 30 s | 30 s | CLK&SP3 | |||||
| MIT0OPSFIN | GE | 300 s | 30 s | CLK&SP3 | ||||||
| NGS0OPSFIN | G | 300 s | ||||||||
| SIO0OPSFIN | G | 900 s | SP3 | |||||||
| Note: a. GRE stands for GPS, GLONASS and Galileo, respectively. b. OSB stands for observable-specific signal bias. c. In the combination and analysis, final products from AC are represented using their ID + “f”, e.g., “CODf” is for the final products from COD. |
||||||||||
Orbit combination results
For the methodology employed in the orbit combination, please refer to “Chen et al., (2023) Multi-GNSS Orbit Combination at Wuhan University: Strategy and Preliminary Products. J Geod. 97, 41”.
The GNSS final orbit products are combined with a sampling rate of 300 s. All results are presented on a weekly basis, with a latency of two weeks.
Orbit combination weight
The orbit combination employs an AC-specific and constellation-specific weighting strategy in which the weight assigned to a particular product depends on its consistency in relation to the combined orbit.
ACs’ orbit transformation parameters
The differences between AC-specific satellite orbits and the combined orbits are expressed in terms of seven Helmert parameters.
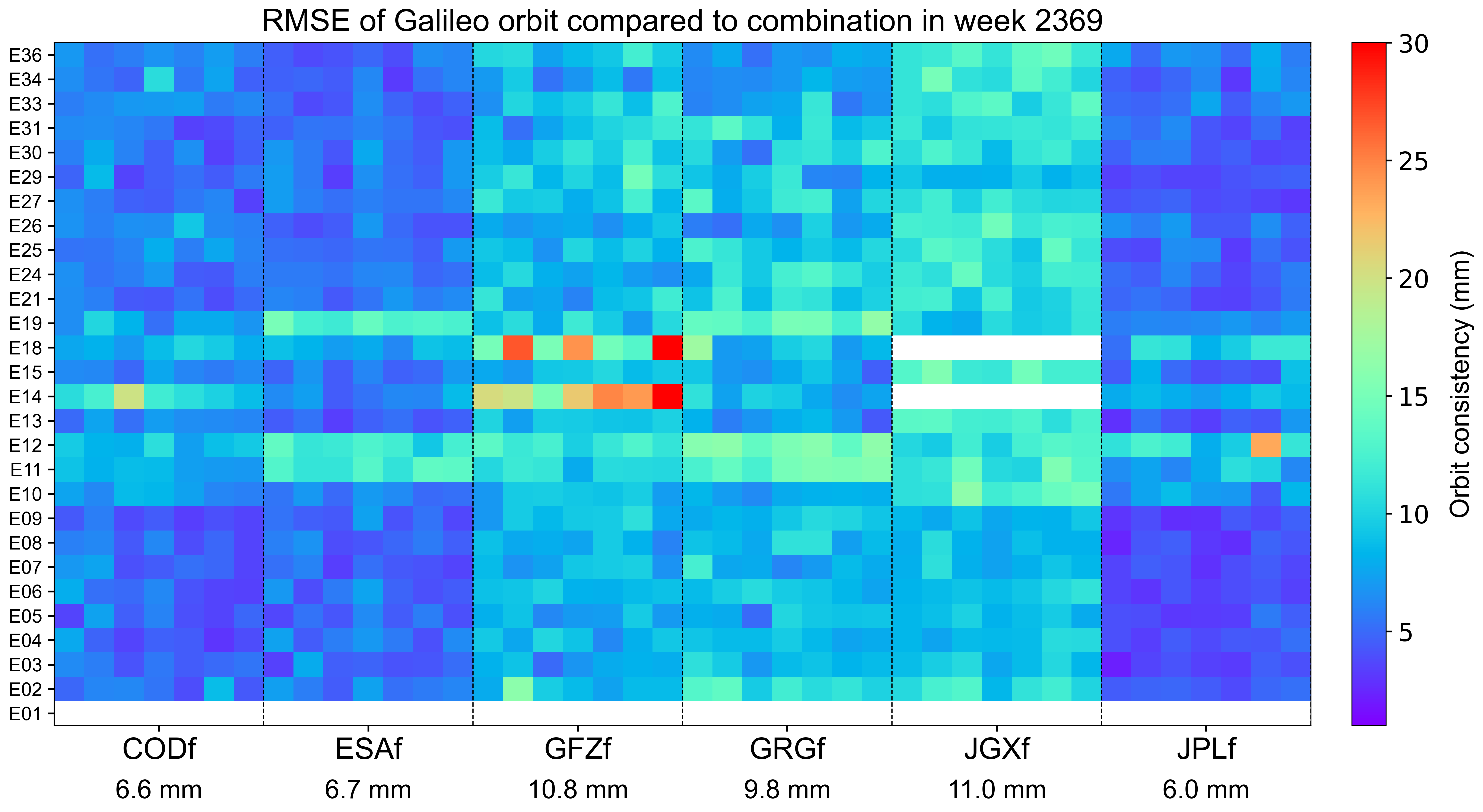
The weekly orbit RMSE
The orbit RMSE refers to the daily combination residuals’ RMSE for each AC with respect to the combined orbit, which reflects the precision of orbit combination and the consistency among contributing ACs. Each grid represents a satellite on a particular day. Blank grids mean unavailable products. The statistics at the bottom indicate the overall RMSE of AC-specific orbit for this week.
Clock/bias combination results
For the method used in the clock/bias combination, please refer to “Geng et al., (2024) Integrated satellite clock and code/phase bias combination in the third IGS reprocessing campaign. GPS Solut. 28, 150”.
The combined orbit products are used as the reference, and the reference attitude is generated by the open-source software GROOPS from TUGraz. The GNSS final clock products are combined with a sampling rate of 30 s. All results are presented on a weekly basis, with a latency of about two weeks.
Clock/bias combination weight
The clock/bias combination employs an AC-specific weighting strategy in which the weight assigned to a specific product depends on its residuals in relation to the combined clock.
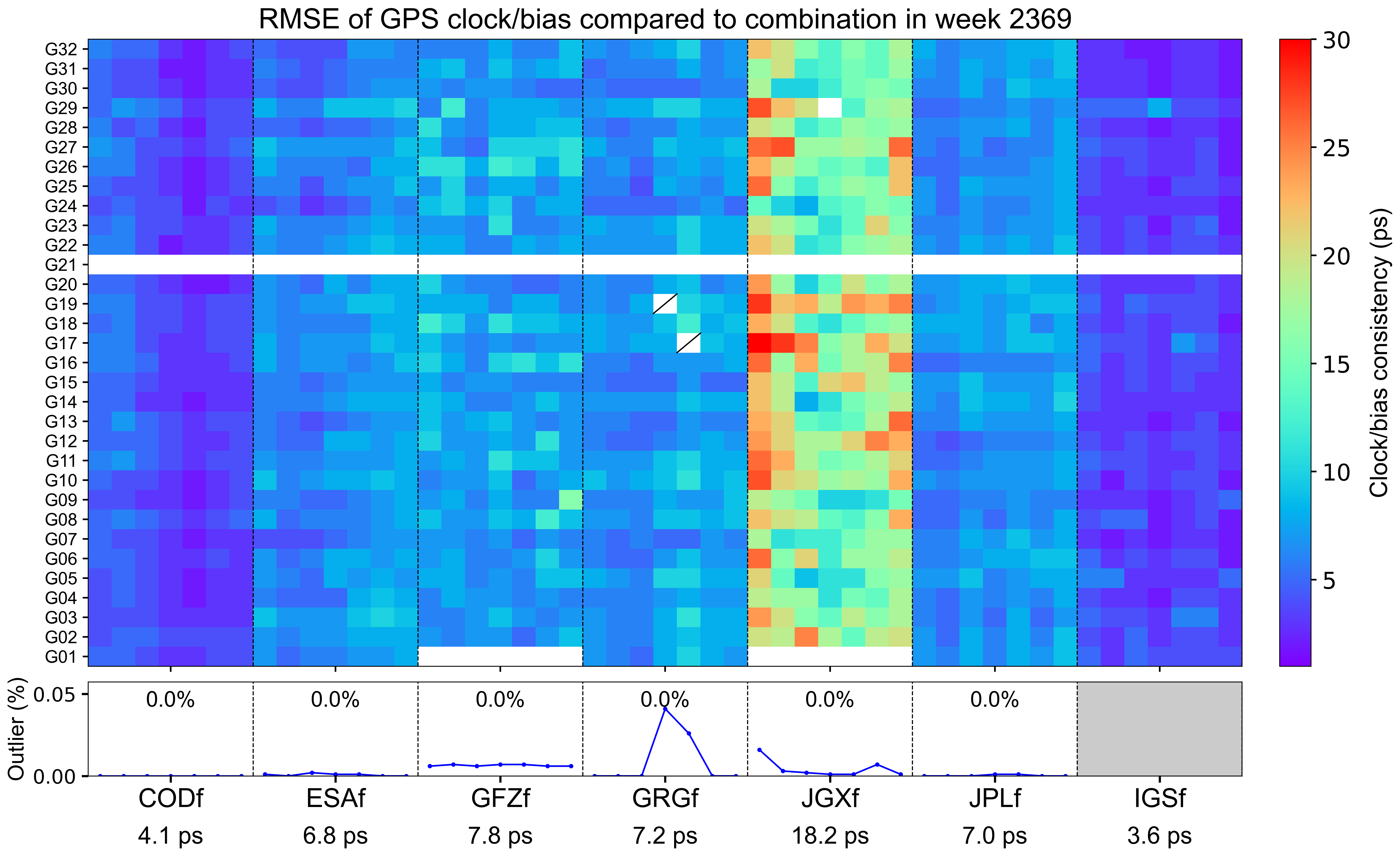
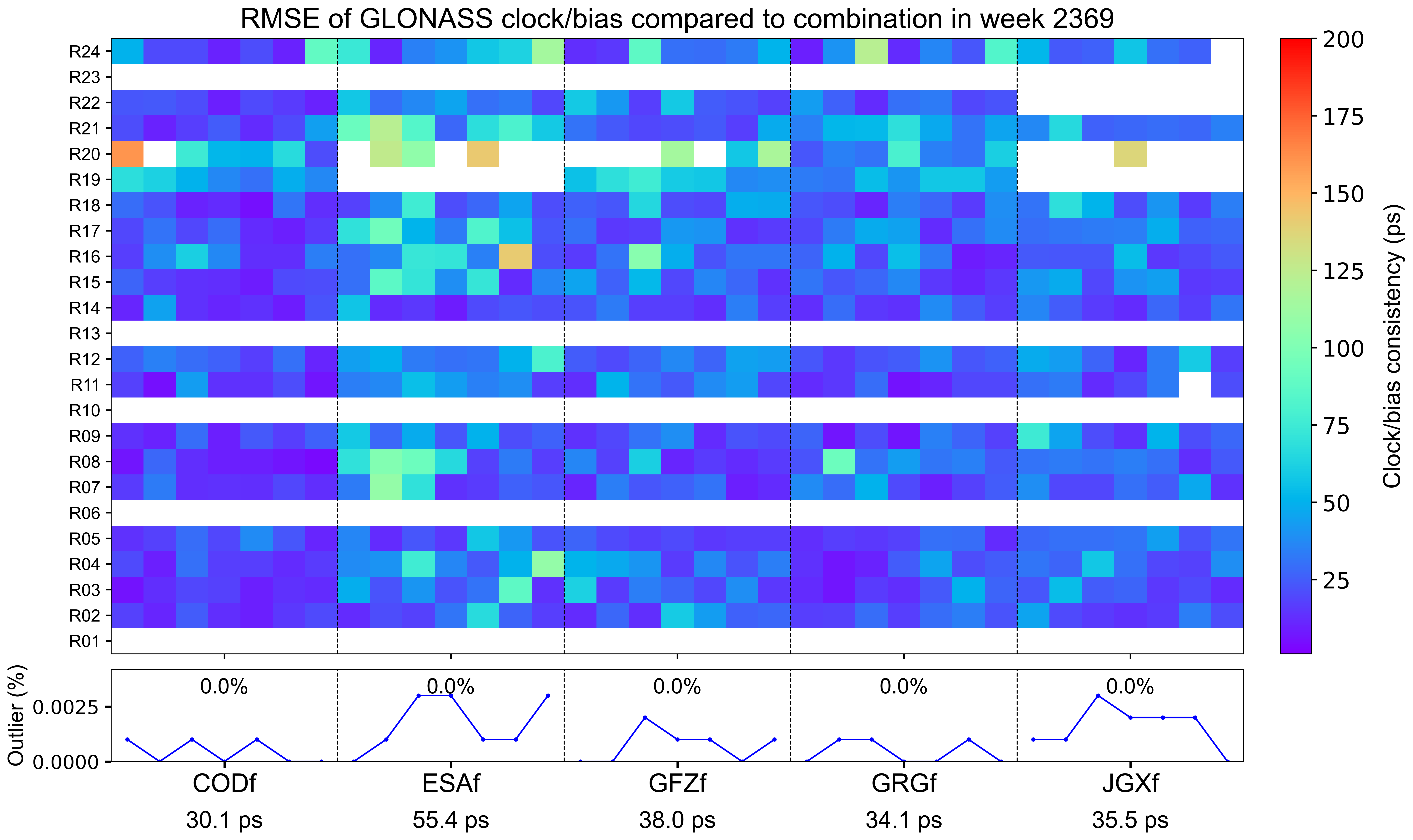
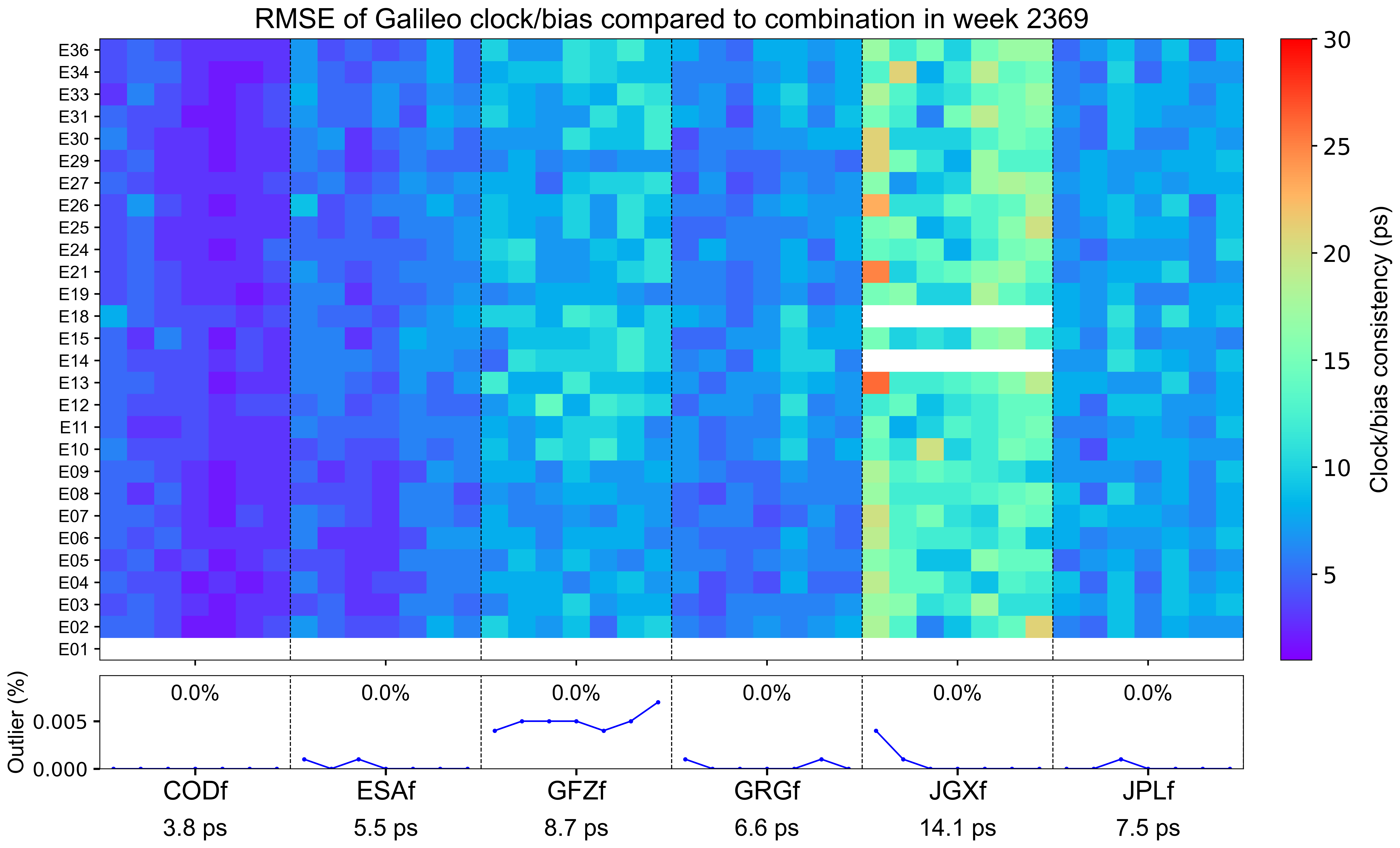
The weekly clock/bias RMSE
The clock/bias RMSE refers to the daily combination residuals’ RMSE for each AC with respect to the combined integer clock, which reflects the precision of clock/bias combination and the consistency among contributing ACs. Each grid represents a satellite on a particular day. Blank grids mean unavailable products and a slash inside means an outlier excluded from the combination. The line chart below shows the outlier rate of satellite clocks per day for each AC, with gray blocks indicating that relevant satellite clocks do not contribute to the combination. The statistics at the bottom indicate the overall RMSE of AC-specific clock/bias products for this week.
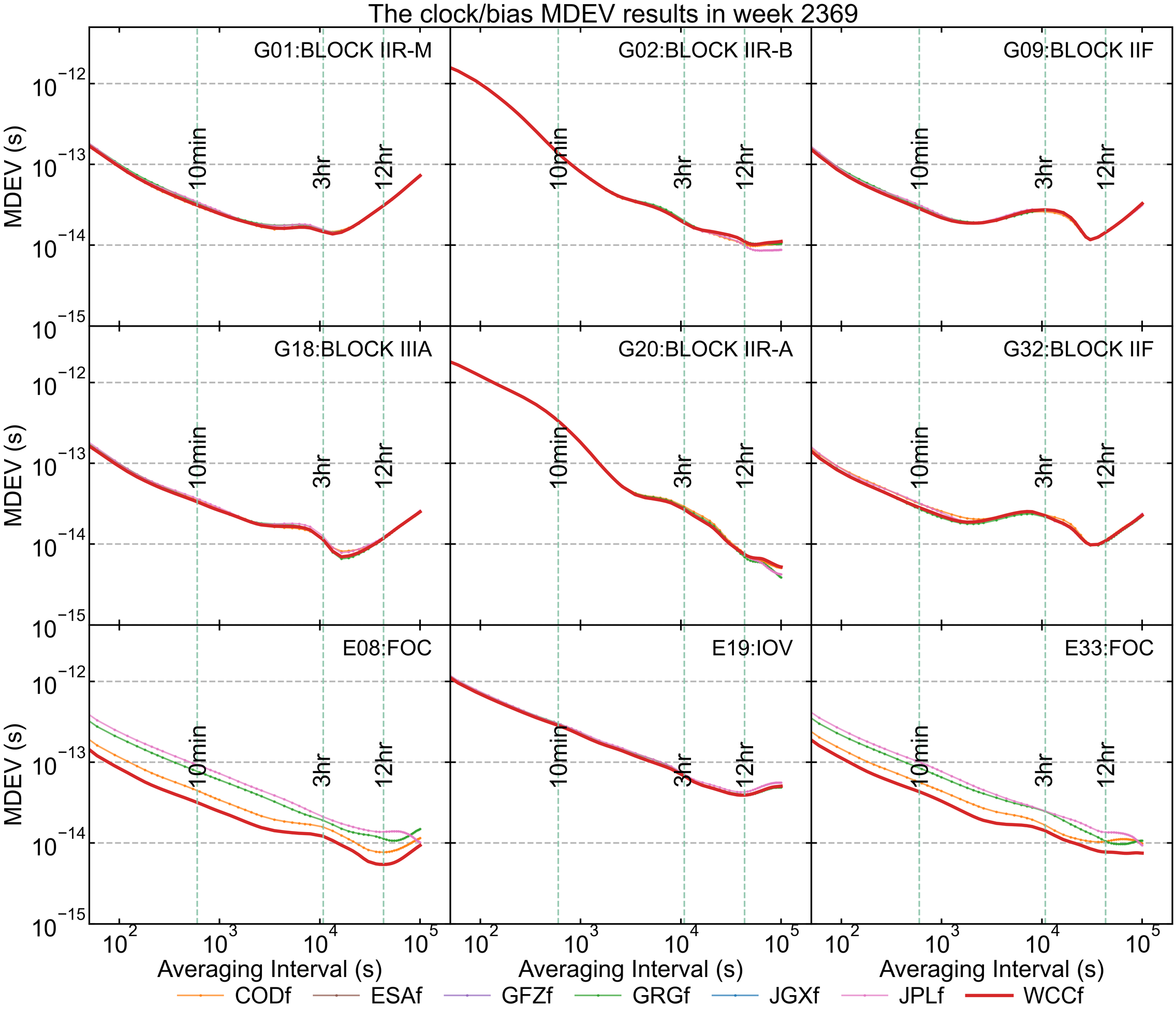
The clock/bias Allan Deviation
The Modified Allan Deviation (MDEV) is used to characterize the frequency stability and noise properties of the integer (legacy)clocks over a week. We present the MDEV values of several representative satellites and stations from each AC and the WCC products. The smaller the MDEV, the better the stability of the clock products. Note that only clock products are used when bias files are unavailable and the GLONASS satellites marked in red only represent legacy clock
Day–boundary discontinuity
DBD (Day-Boundary Discontinuity) refers to the difference between the satellite products at the 24:00 epoch and its counterpart on the next day at the 00:00 epoch. Before releasing final products, we align them to the preceding day’s products to remove DBDs. The alignment method refers to “Lin et al. (2025) Aligning GPS/Galileo/BDS satellite integer clock products across day boundaries for continuous time and frequency transfer. J Geod. 99, 35”.
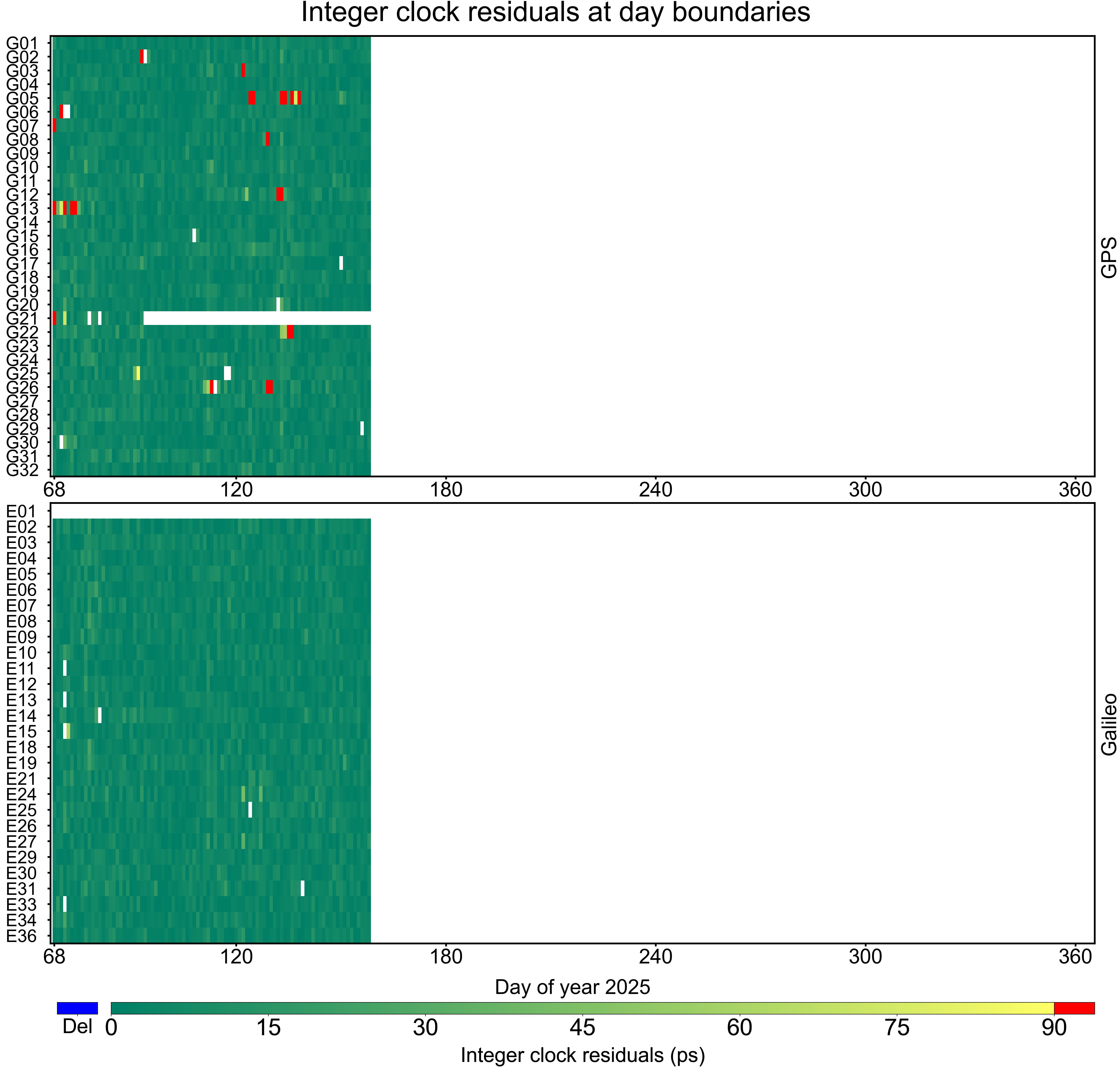
Integer clock residuals at day boundaries
The integer clock day-boundary residuals serve as diagnostics of DBD alignment performance. The figure shows the cumulative integer clock residuals of the WCC products to date to reflect the overall DBDs of the WCC. Each grid represents a satellite on a particular day. A blank grid indicates that there is no available 24:00 epochs, blue indicates missing bias thus is deleted during DBD alignment, and red indicates values exceeding colorbar limits.
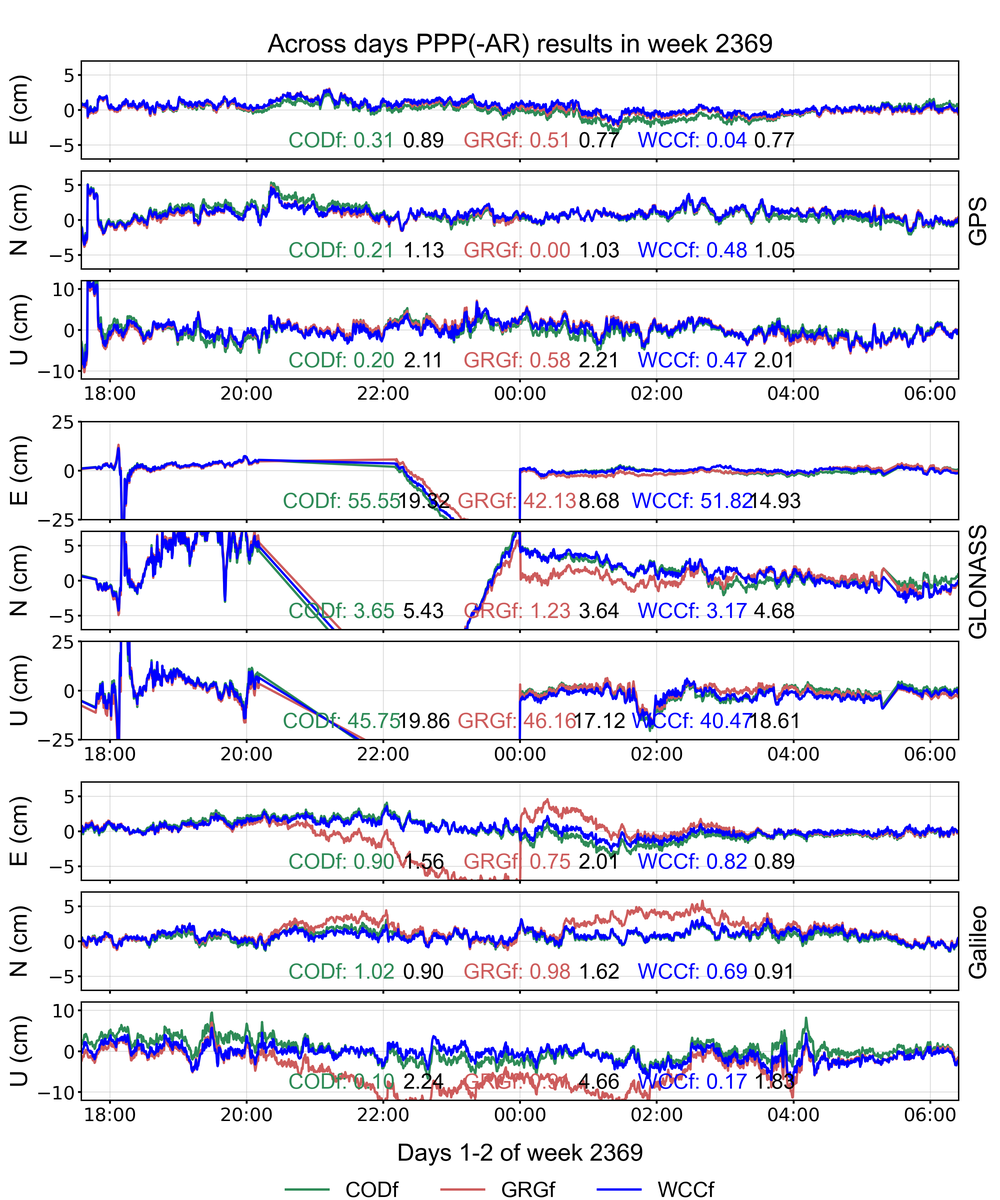
Kinematic PPP-AR across days
The DBD-removed combined clock/bias products can ensure the continuity of integer ambiguities across day boundaries during PPP processing. Naturally, the DBD-removed clock/bias products can recover the continuity of kinematic positioning coordinate series. We processed kinematic PPP solutions for ten stations using PRIDE PPP-AR, covering 6 hours before and after the 24:00 epoch on a specific day of this week. “WCC” represents the combined products. The numerical values in the figure indicate day-boundary discrepancies and the RMSE of coordinate time series (black). Note that the GLONASS system is incapable of alignment, and this only demonstrates its dynamic positioning performance.
PPP/PPP-AR validation
The GPS/GLONASS/Galileo data with a sampling rate of 300 s from 10 globally distributed stations are processed for PPP/PPP-AR in a static mode with the PRIDE PPP-AR software. The fixing rate and position precision of each single constellation solution are presented in the figure below. IGS daily SINEX products are used as reference solution. “WCC” stands for the combined products.
Last Updated on 1 Dec 2025 01:39 UTC